Diabetic Retinopathy
WHAT IS DIABETIC RETINOPATHY
Diabetic retinopathy is a diabetes-related eye disease that affects the blood vessels in the retina, the light-sensitive tissue at the back of the eye. It is caused by high levels of blood sugar damaging the small blood vessels in the retina, leading to a reduction in blood flow to the retina and the growth of abnormal blood vessels. Over time, these abnormal blood vessels can leak fluid and blood into the retina, leading to vision loss and potentially blindness.
Diabetic retinopathy often develops gradually, and many people with diabetes may not experience any symptoms in the early stages. However, as the disease progresses, symptoms may include blurred vision, dark or empty areas in the field of vision, and difficulty seeing at night.
To prevent diabetic retinopathy, it is important for individuals with diabetes to maintain good control of their blood sugar levels, blood pressure, and cholesterol. Regular eye exams are also essential, as early detection and treatment can help to prevent vision loss. Treatments for diabetic retinopathy may include laser therapy, medications, or surgery, depending on the severity of the disease.
WHAT CAN AN OPTOMETRIST DO FOR DIABETIC RETINOPATHY
An optometrist can play an important role in the management and treatment of diabetic retinopathy. They can:
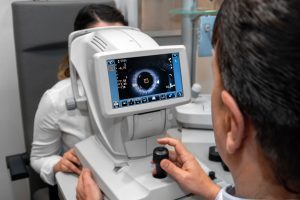
- Conduct regular eye exams: An optometrist can perform regular eye exams to monitor the progression of diabetic retinopathy and detect any changes in the retina. Early detection and treatment are crucial in preventing vision loss. They can alert your primary care physician or endocrinologist to changes in the vascular system that may be undetectable by bloodwork or other means.
- Prescribe corrective lenses: If diabetic retinopathy has caused vision problems, an optometrist can prescribe corrective lenses to help you see more clearly.
- Make referrals for treatment: An optometrist can make referrals for specialized treatments, such as laser therapy or injections, to manage the progression of diabetic retinopathy.
By seeking the help of an optometrist, individuals with diabetic retinopathy can receive personalized care to manage the condition and reduce the risk of vision loss. If you have diabetic retinopathy, it’s important that you get professional help to manage the condition.
West Edmonton Vision Clinic
Visit our vision clinic in central West Edmonton for comprehensive eye exams, contact lens fittings, glasses, and more. Louie Eyecare Centre is dedicated to providing the highest quality optometric services and products to our patients. Our team of experienced optometrists is here to help you with all of your eye care needs. Schedule an appointment today!
Clinic Hours
Monday Closed
Tuesday 9:00-5:00
Wednesday 9:00-5:00
Thursday 9:00-5:00
Friday 9:00-5:00
Saturday 9:00-2:00
Closed Sunday / Holidays
OUR CLIENTS' FEEDBACK
Frequently Asked Questions
Wearing glasses or contacts can indeed affect dry eye symptoms, but the impact varies. Glasses can help shield the eyes from environmental factors that exacerbate dry eye, such as wind or air conditioning. On the other hand, contact lenses can sometimes worsen dry eye symptoms by absorbing tear moisture or by causing irritation. Certain types of contact lenses are designed to be more breathable and retain moisture better, which may be suitable for people with dry eyes. It’s crucial to discuss with an eye care professional to find the most appropriate type of contact lens or glasses. Proper care and hygiene when using contacts, along with regular breaks from screen use, can help minimize dry eye symptoms.
Dry eye syndrome can be both a temporary condition and a chronic disease, depending on its cause and severity. Environmental factors or certain life situations, such as screen use or air travel can cause temporary dry eye. Chronic dry eye, on the other hand, may result from systemic diseases, medication side effects, or age-related changes in tear production. Management and treatment can alleviate symptoms, but chronic dry eye often requires ongoing therapy. It’s important to consult with an eye care professional for an accurate diagnosis and treatment plan. Understanding the underlying cause is key to determining whether dry eye syndrome will be a temporary issue or a chronic condition.
Yes, some specific exercises and therapies can help relieve dry eye symptoms. Blinking exercises, for example, can help improve meibomian gland function and tear film stability. Warm compresses applied to the eyes can also stimulate tear production and release oils from the glands in the eyelids. Gentle eyelid massages can help spread the oils evenly across the eye surface, reducing dryness. Using a humidifier to add moisture to the air and taking regular breaks to rest the eyes during screen time can also be beneficial. Newer technologies such as IPL (Intense Pulsed Light) and RF (Radio Frequency) are also becoming available. Consulting with an eye care professional for personalized advice on exercises and therapies is recommended.
Sleep plays a crucial role in managing dry eye syndrome. Poor sleep can lead to insufficient eye lubrication and worsening dry eye symptoms. During sleep, the eyes rejuvenate and produce the moisture needed for the next day. Good sleep hygiene practices can help ensure the eyes are well-rested and hydrated. It’s also important to avoid sleeping with any airflow directly hitting the face, as this can dry out the eyes. Establishing a regular, restful sleep schedule can significantly improve dry eye symptoms.
Indeed, some medications can exacerbate dry eye symptoms. Diuretics, antihistamines, antidepressants, and some blood pressure medications are known to reduce tear production or alter tear composition. It’s important to review any current medications with a healthcare provider to determine if they could be contributing to dry eye symptoms. Sometimes, alternative medications with fewer dry eye side effects can be prescribed. Always consult with a healthcare professional before making changes to medication regimens. Patients should also stay hydrated and consider using artificial tears if taking medications known to cause dryness.
Yes, it is quite common for dry eye symptoms to worsen in certain weather conditions. Dry, windy, or smoky environments can lead to increased tear evaporation, exacerbating symptoms. Conversely, high humidity can sometimes alleviate dry eye symptoms because the air is more saturated with moisture. Cold weather, especially during winter when indoor heaters are used, can also dry out the eyes. It’s advisable to use humidifiers in such conditions to maintain indoor humidity levels. Wearing wraparound glasses or protective eyewear outdoors can help shield eyes from harsh conditions.